You can connect a Raspberry Pi to your Arduino with a USB cable and read the Serial Output into Variable Values.
Prerequisites:
Functional Parts in the Project:
- Arduino Uno – https://store.arduino.cc/usa/arduino-uno-rev3
- Breadboard Kit – https://amzn.to/2Xih5ei
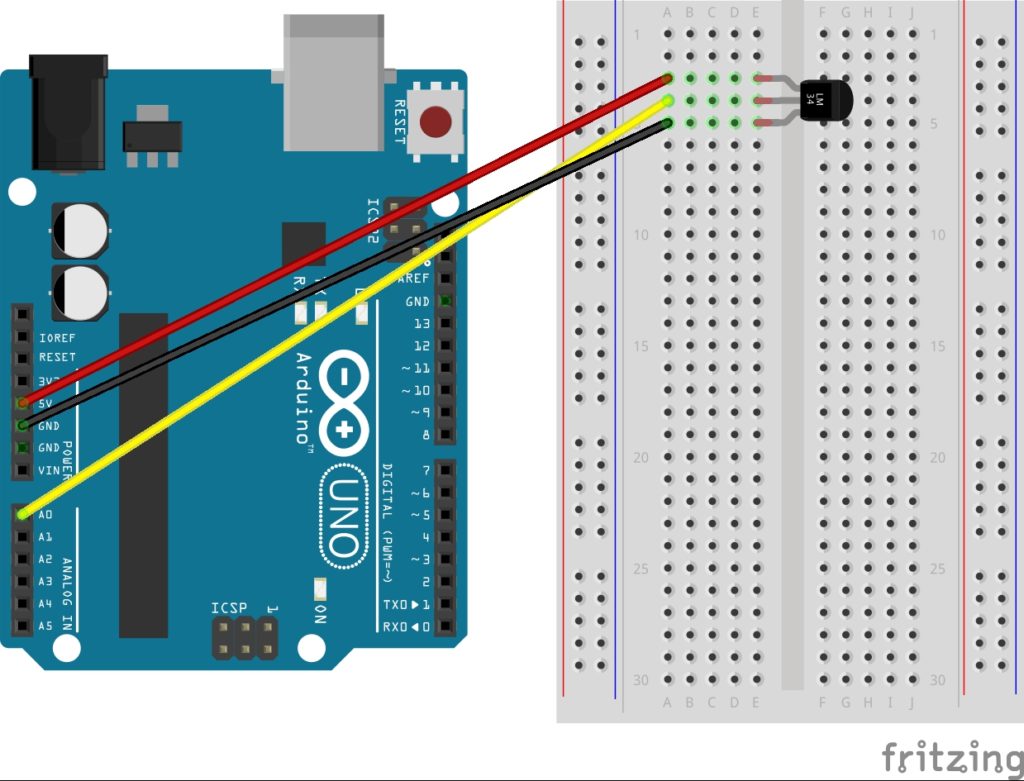
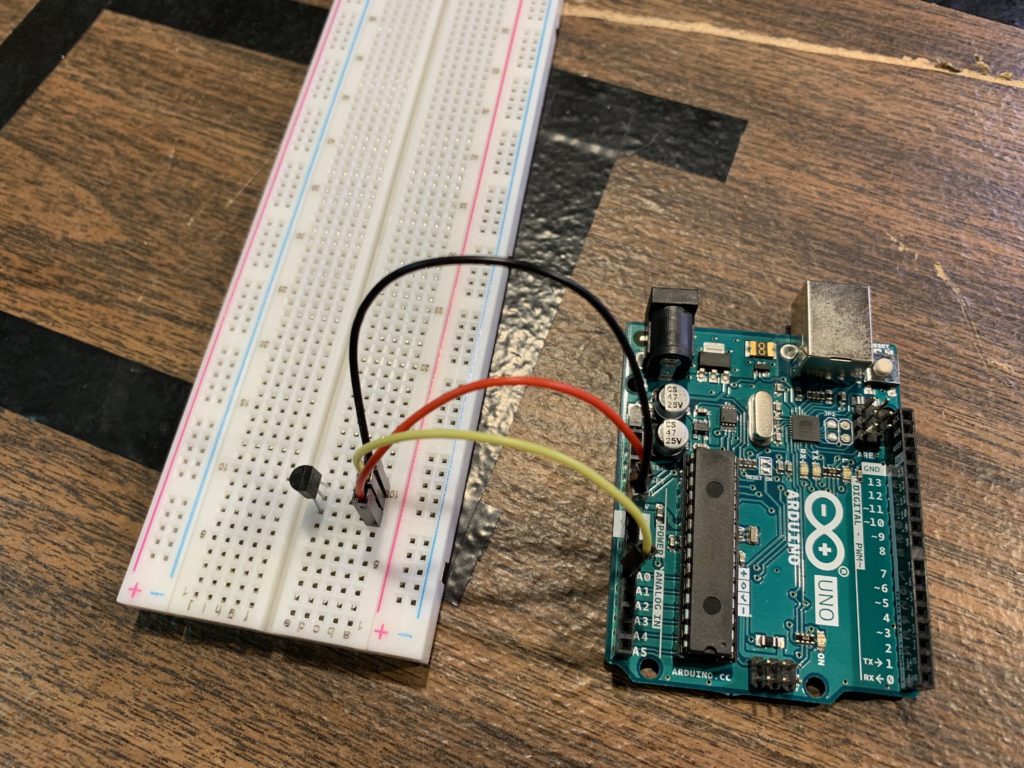
- Analog Temperature Sensor – https://amzn.to/2Rkkl3k
- Raspberry Pi 4 B
- USB Cable
Python Script
import serial
if __name__ == '__main__':
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyACM0', 9600, timeout=1)
ser.flush()
while True:
if ser.in_waiting > 0:
line = ser.readline().decode('utf-8').rstrip()
print(line)Find the connection to the Arduino. Type in the Terminal and find ttyACM0 or ttyACM1. (If you unplug the Arduino and plug it back in the address may iterate up to ACM1 instead of ACM0)
ls /dev/tty*Arduino Sketch (Any Sketch that outputs in Serial will work)
#define sensorPin A0
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
int reading = analogRead(sensorPin);
float voltage = reading * 5.0;
voltage /= 1024.0;
float temperatureC = (voltage - 0.5) * 100 ;
float temperatureF = (temperatureC * 9.0 / 5.0) + 32.0;
Serial.print(voltage); Serial.print(" volts - ");
Serial.print(temperatureC); Serial.print(" degrees C - ");
Serial.print(temperatureF); Serial.println(" degrees F");
delay(1000);
}



Be the first to comment